One of the metrics we use to evaluate a peptide map is sequence coverage. Sometimes we’re really only interested in a few key peptides, but other times it’s important to see the entire protein sequence. So what can we do when we don’t have 100% sequence coverage?
The first step is to review your data and the sequence of your protein to see how much of the sequence is missing and what theoretical peptides weren’t detected.
As in the first example below, are the missing pieces single amino acids, or very small di- or tri-peptides? For example, does the sequence contain consecutive lysine residues? Reversed-phase chromatography typically used for peptide mapping won’t retain these species.
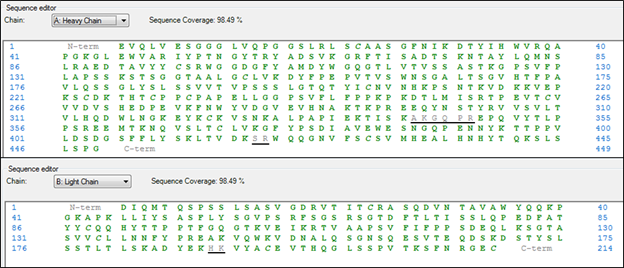
This peptide map of Trastuzumab has a sequence coverage of 98.49% for each chain. The gray underlined amino acids are the portions that weren’t detected. A single dipeptide (HK) is missing from the light chain, while two dipeptides (AK and SR) and a tetrapeptide (GQPR) are missing from the heavy chain.
There are three possible next steps in this case:
- If those residues are insignificant, we can move forward with the existing data and peptide mapping method.
- If it is critical to detect those amino acids, there are two possibilities:
- Choose a different digestion enzyme that produces different cleavage sites. Trypsin is often the go-to protease for its predictability, but there are lots of other options out there.
- Change the digestion protocol with the aim of producing an incomplete digestion, for example, by shortening the digestion time.
On a related note, is it the small, hydrophilic peptides that weren’t detected? Not all C18 columns are the same, and some will be more retentive than others. A different C18 column may be the answer.
Are the missing peptides very large or hydrophobic? For example, both the light and heavy chain in Trastuzumab have a complementarity determining region comprising a very long, hydrophobic peptide that can be challenging to detect.
In this case, how to recover these peptides depends on where the peptide is being lost.
- The peptide could be sticking to any surface it comes in contact with, including pipette tips, sample storage tubes, or autosampler vials. Switching suppliers or materials may help.
- Take a fresh look at your sample prep protocol – could a particularly hydrophobic peptide be precipitating? Remember that an acetonitrile crash is an easy and therefore popular way to precipitate proteins from solution.
- If the peptide is sticking to the column, there are a few things to try:
- Can you go to a higher percent organic mobile phase? Or add a stronger organic solvent such as isopropanol to your (probably) acetonitrile mobile phase? There’s an example of this shown below.
- Switching up the column chemistry may be the solution – again, more on that next time.
- Finally, unrelated to where the peptide may be getting stuck, go back to the sequence one more time. Are there missing cleavages? An adjustment to the digestion protocol or a different protease may be helpful. (Or maybe even simpler, did you allow for missed cleavages when you searched the data? Maybe the answer is as simple as a checkbox!)
This mAb peptide map below has only about 75% sequence coverage – definitely a problem. Looking at the sequence below, we see that there are a few very large peptides missing. One missing peptide from the light chain is 42 residues long, and another missing from the heavy chain is 63 amino acids! The average tryptic peptide is only 6 residues1, and methods are generally developed accordingly. In this case, the gradient didn’t go to high enough organic – only 19% acetonitrile.
It’s next to impossible to catalog every reason for a missing peptide. Sometimes a step that recovers one missing peptide causes another to be lost, necessitating an approach like a combination of digestion enzymes. Today we’ve really focused on digestion and chromatography method adjustments, though sometimes a different C18 column may be the answer. But hopefully this food for thought is helpful!
Until next time –
Anne
References:
- Giansanti, L. Tsiatsiani, T.Y. Low, A.J.R. Heck. Six alternative proteases for mass spectrometry-based proteomics beyond trypsin. Nature Protocols, 2016.
Keywords: Bio columns liquid chromatography, tips and tricks, peptide mapping, reversed-phase, troubleshooting, AdvanceBio blog