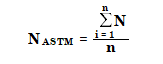How to Check the signal-to-noise ratio with Agilent OpenLab CDS (version 2.x) - Chromatography Software Articles - Chromatography Software Portal - Agilent Community
Lists both Peak to Peak and ASTM as using the same formula for calculation S/N. What is the difference between these two parameters in the software?
Is one more aligned to USP <621> which also gives S/N ratio calculation as 2H/h?
Thanks