Hello
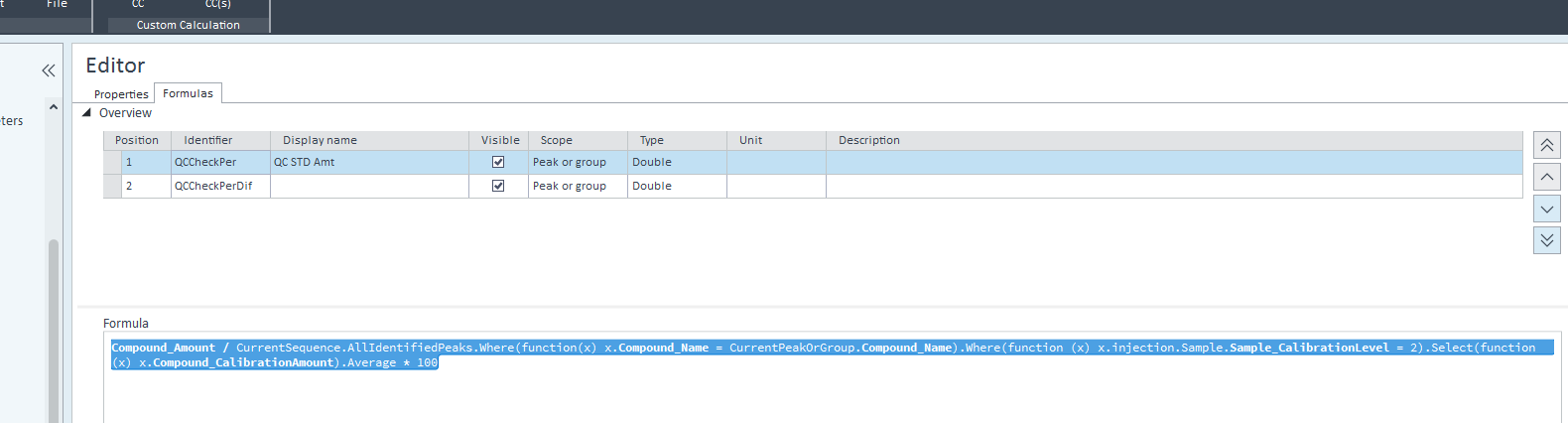
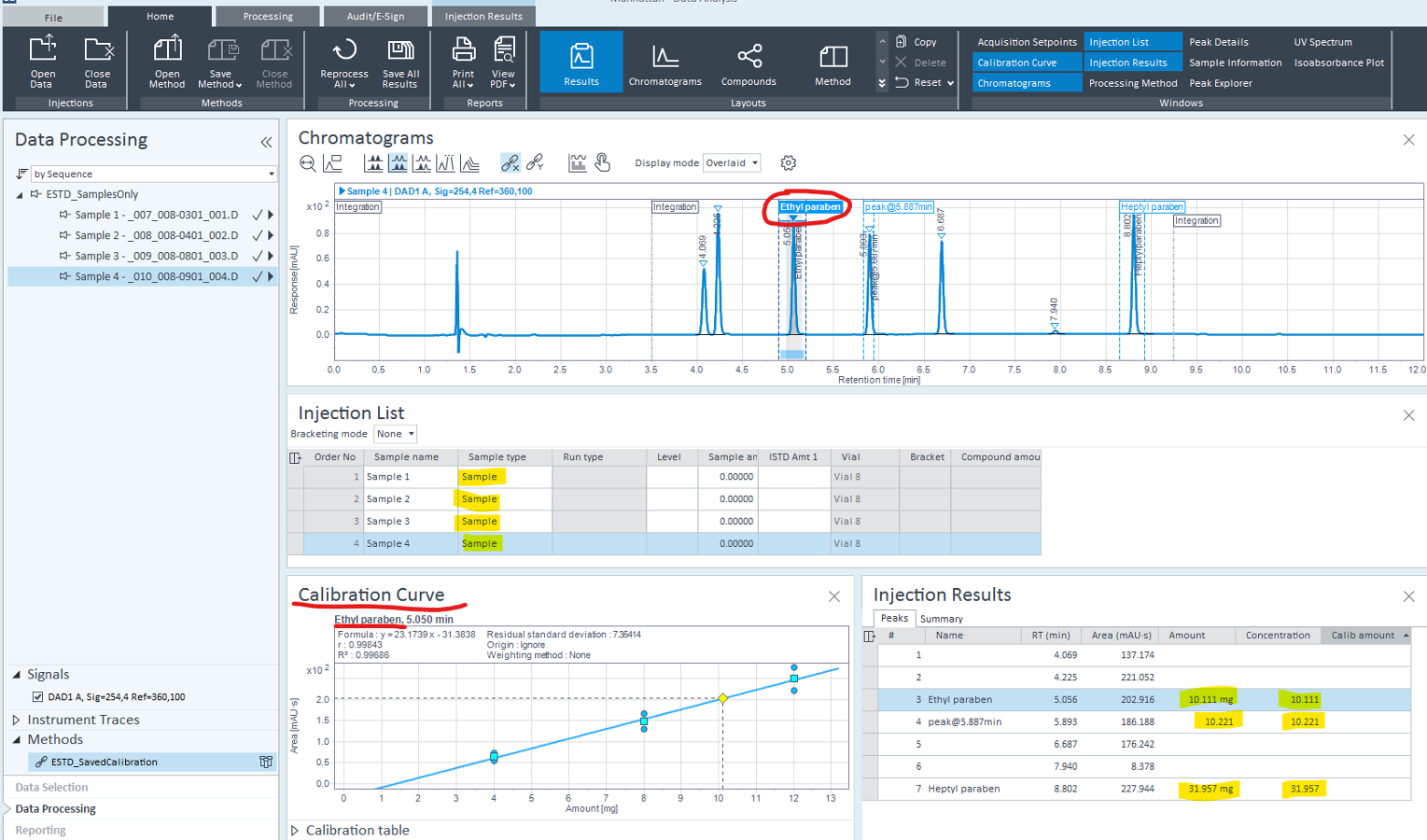
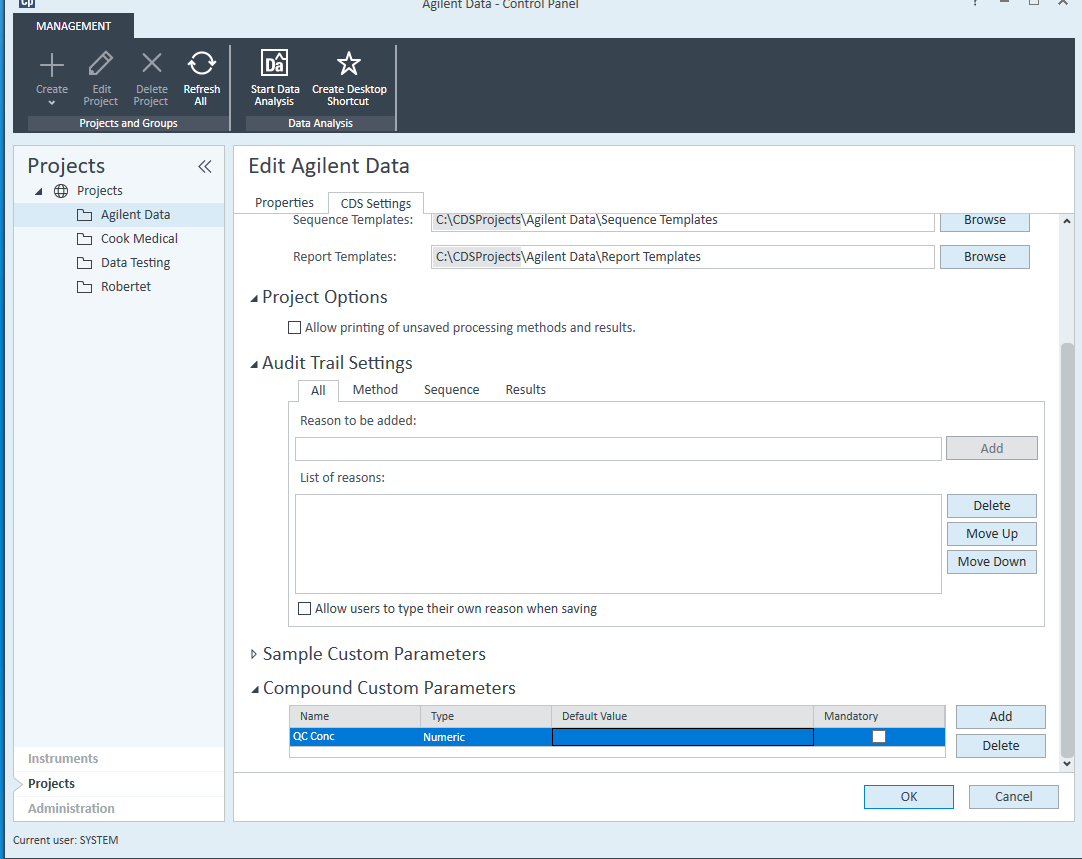
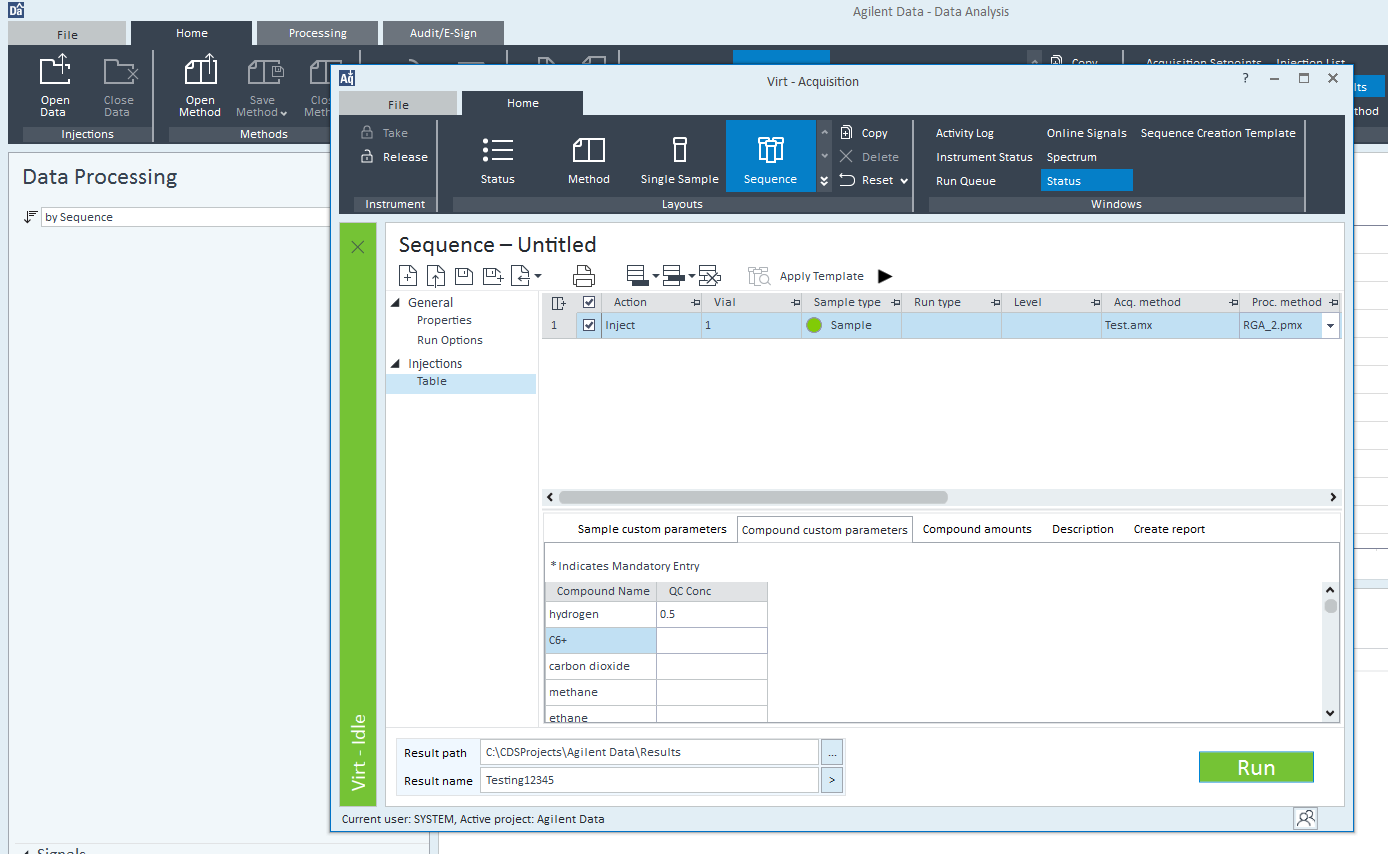
I have a processing method where there is some calibration amount entered for a compound. When I am processing a sequence where there are no standards, only QC checks, I cannot get the Compound_CalibAmount values from the processing method and use it in reporting. Is there a way?
Thank you
Martin